
Brief overview of course content with an introduction to BlueJ (IDE), Java, Pseudocode and Algorithms

We introduce classes, objects, methods, parameters, variables, data types, files in java and the JVM

We continue our exploration of classes and objects and introduce method signatures, return types, class naming conventions and access modifiers

In this presentation we continue exploring elements of classes and the Java language including how source code is written and presented. We also introduce conditional statements, which offer choices between different actions as the program executes.

We examine some of the components of the ticket machine program. We look at some further elements of the Java language such as local variables and scope, operators, parameters and comments.
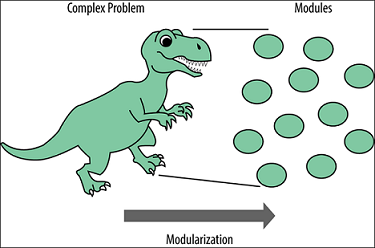
Abstraction means ignoring details for the moment and concentrating on the problem at a higher level. Modularization comprises subdividing the problem into manageable parts each of which interacts in well-defined ways into the overall project.
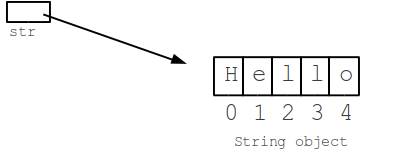
Here we focus on the String class and investigate, through its methods, the types of operations we can do on a String.

Here we will cover some miscellaneous items such as static variables, static methods, Javadoc comments, debugger and compound assignment statements.
We now introduce collection classes and control flow techniques to traverse such collections. Specifically we examine the ArrayList class and how to use the class to manage and manipulate data.
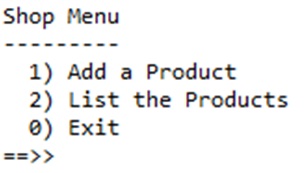
We will look at adding a menu to the Shop project that we explored in labs. New concepts include sentinel-based loops, switch statements and the Scanner class.
/talk-a/lecture_10.png)
We will look at speeding up the testing of our Shop app by using JUnit Test Fixtures.
/talk-b/lecture_11.png)
We will learn how to incorporate the CheckStyle functionality into BlueJ. This will help us to write code that compiles 100% to Java's coding standards.

Begin exploring the Eclipse Integrated Development Environment (IDE). We will also look at the Java Virtual Machine (JVM) and the main method.
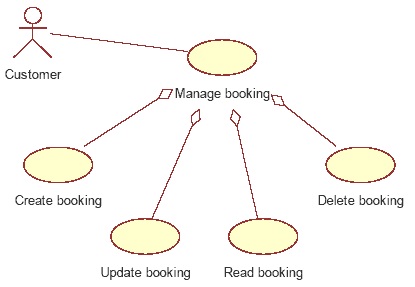
We will introduce you to the Create, Read, Update and Delete (CRUD) Process.

We will introduce you to XML and show you how to serialize objects from Java to an XML file and read them back into your Java program.

We will show you, by using try and catch blocks, how to stop your program from crashing when invalid user input is entered.

We explore the concept of primitive arrays and iterating over its elements using for, for-each and specific types of while loops.

We will start developing a simple console-based tech support system that will always respond with the phrase "That sounds interesting. Tell me more...".

We will continue developing the simple console-based tech support system. However, in this version, we will have more meaningful, randomised responses for the user.

We will continue evolving the simple console-based tech support system. However, in this version, we will reply to the user with a context sensitive response, based on their input.
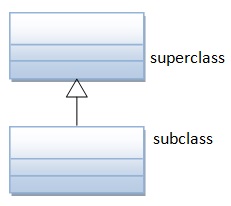
We will start investigating inheritance which is one of the key principles in Object Oriented programming.

We will continue looking at inheritance and cover polymorphism, overriding and dynamic method lookup.

We will look at structuring our apps using packages and re-usable utilities. We will also look at using Wrapper classes to parse String input as a specific type.
/talk-1/lecture_23_pbl.jpg)
We will introduce a different approach to learning, called Problem-based Learning (PBL).
/talk-2/lecture_24-hare-and-tortoise.jpg)
We will introduce the board game, Hare and Tortoise, that you will build for your assignment.
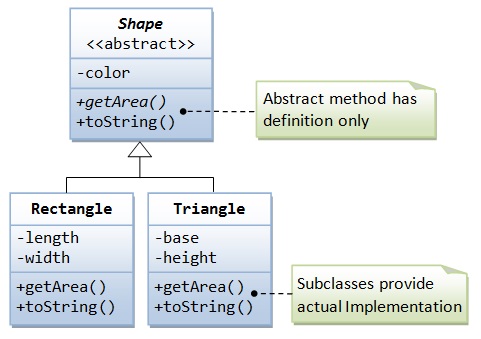
We will start implementing abstraction in our inheritance hierarchy for the Network system.

We will introduce the concept of TDD, Unit Testing and the JUnit Framework.

We will demonstrate how to use the JUnit Framework to test DVD.java.

Having tested DVD.java using the JUnit Framework, we will now cover the terminology used in this process (assertions, annotations and fixtures).

Here we will cover the Four Phase Test and present a more complicated JUnit test.

Here we will review the DVDTest.java class and develop JUnit tests for more classes in the DVD app.
We will do a recap of abstract classes and methods.
By examining the Deadly Diamond of Death, we will reason why Java does not allow Multiple Inheritance.
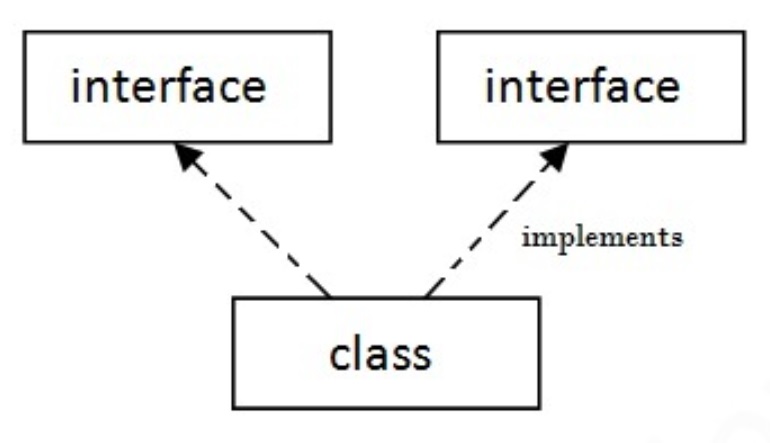
We will introduce the concept of Interfaces, discuss their syntax and provide a simple example.
We will delve deeper into Interfaces by using predefined Interfaces in our programs and also writing our own Interfaces.
/talk-1/Assginment_3.jpg)
The specification for Assignment 3 (worth 40% of your grade for this semester).