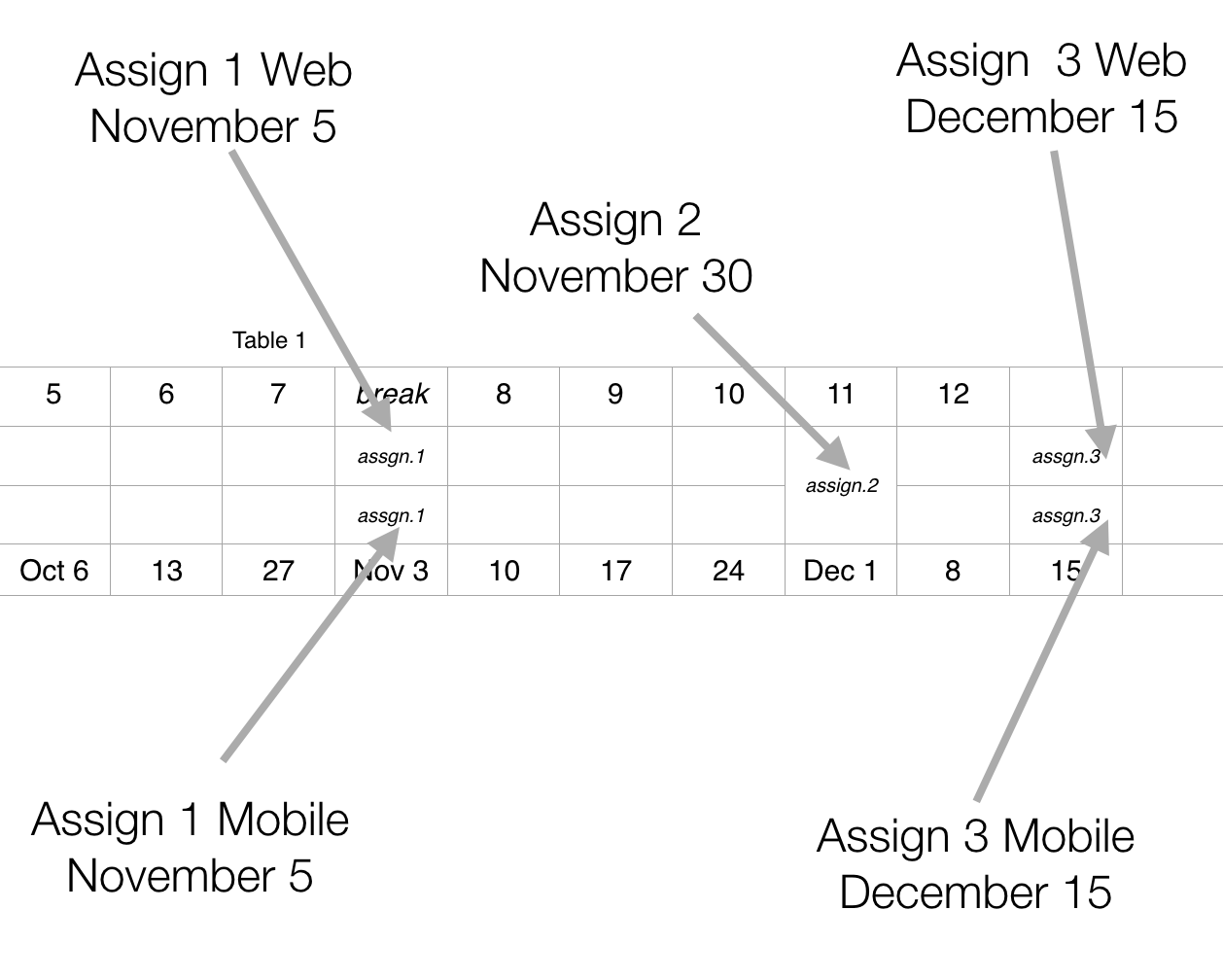
The Calendar for the three assessments in this module

The specification for Assignment 1
The specification for assignment 2
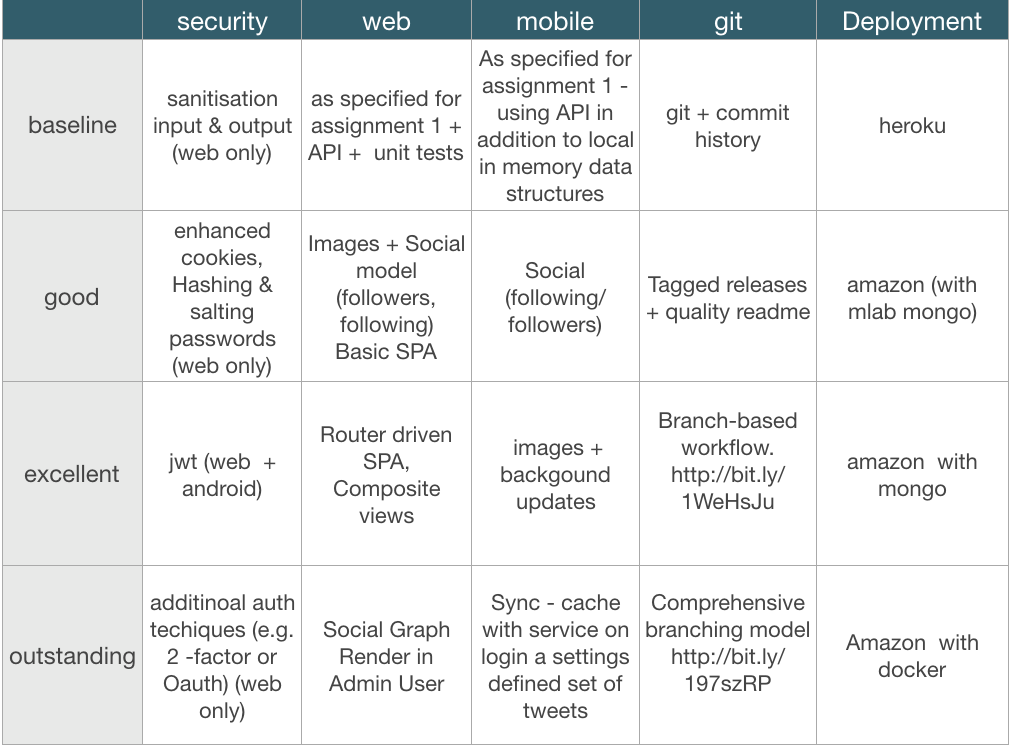
The specification for Assignment 3 + summary of grading approach
A review of the the evolution of a web site from simple unstyled pages to a reasonable simple but appealing layout.
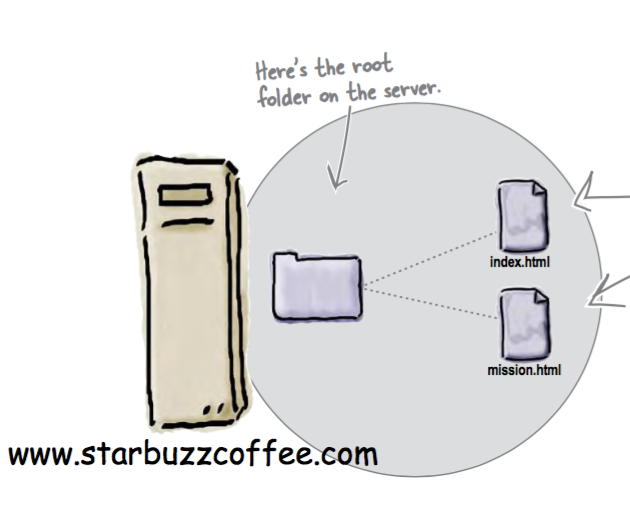
Deploying a site involves understanding a little more about Clients & Servers, Hosting Providers, Domain Names, Transferring the Sites Files, HTTP and Absolute & Relative Paths

Harp.js and Surge.sh are the two services we will use to server the page locally, and also to deploy it to a public web server.
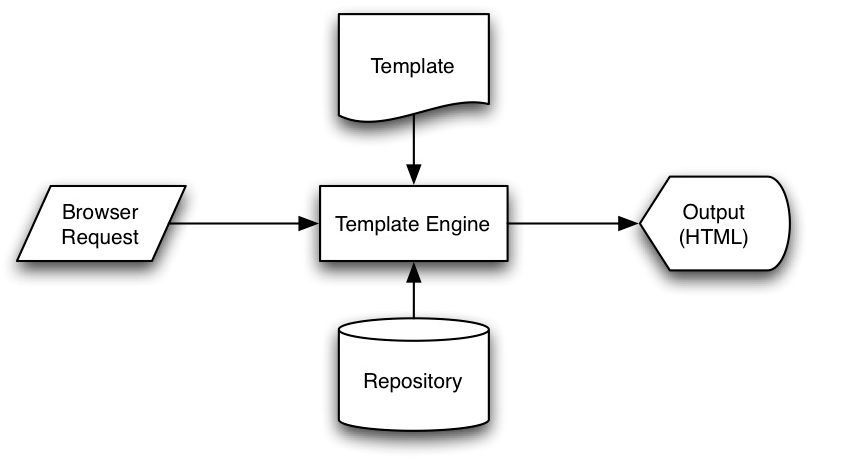
The EJS template system implements mechanisms for assembling sites from templates - which are called 'partials' in EJS. Additionally, there is a complimentary 'layout' mechanism for reusing entire page structures.
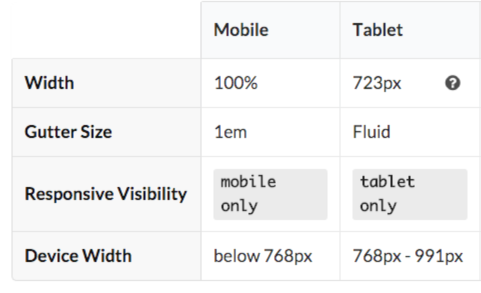
An overview of the container and segments styles in the framework

An exploration of the Grid and Image styles.
An exploration of the Tables
Our final tour of the Semantic-UI library - with a focus on icons, variations in segments and responsive grids

Introduction to the the role of CSS Preprocessors and build tools
Our final tour of the Semantic-UI library - with a focus on icons, variations in segments and responsive grids
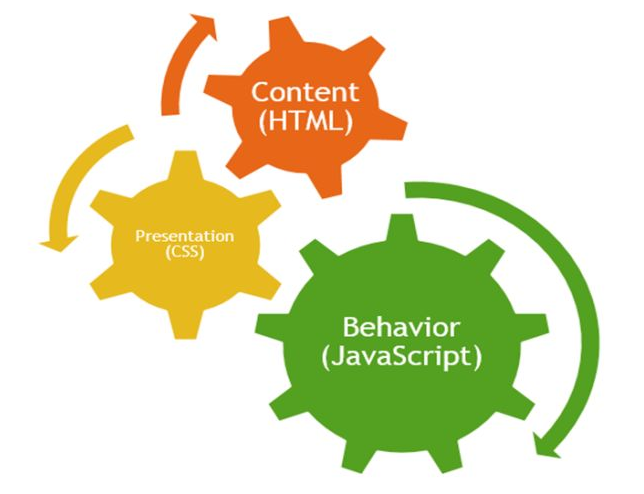
JavaScript, an introduction to the language of the web.
Continuing introduction to the language including the topics of identifiers, operators and contol flow techniques.
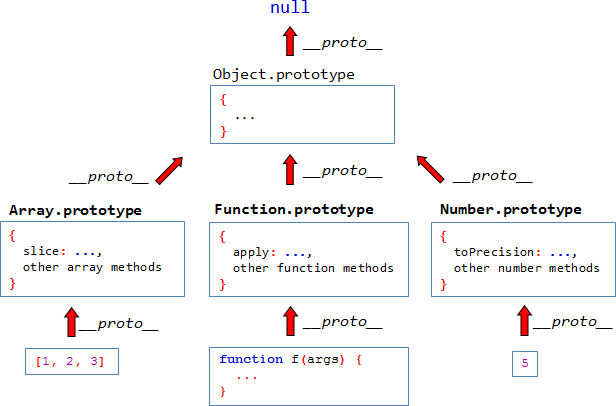

Simple JavaScript client-side applications. Introducing Chrome Developer tools.

The DOM: Javascript manipulates the contents of the web page through a standard abstraction called the Document Object Model (DOM), hence the reason for this brief introduction.

jQuery: although not as popular as it once may have been, rumours of its death have likely been greatly exaggerated. Undoubtedly losing ground to modern frameworks. it will still probably be in widespread use for quite some time yet.

Concluding our introduction to JavaScript with a brief discussion about Ajax.
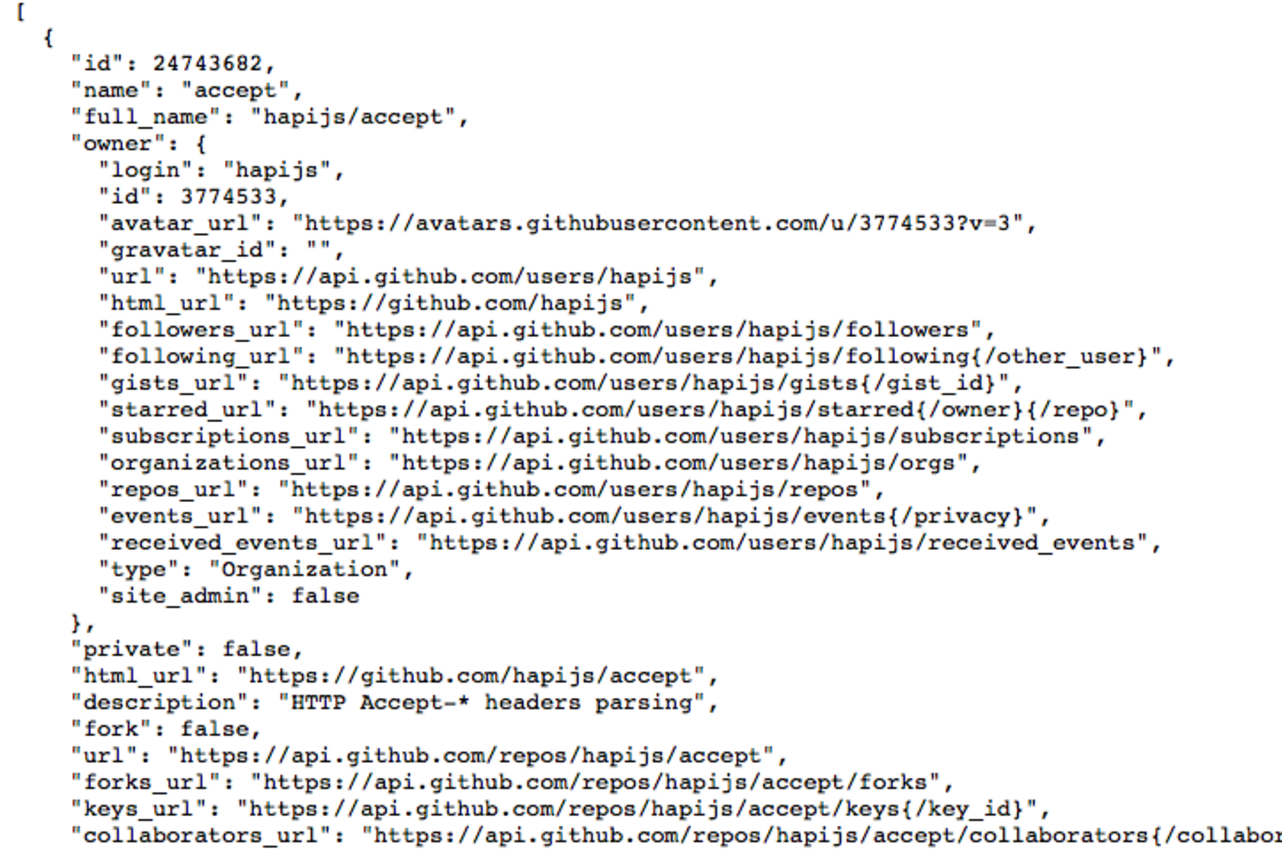
APIs in Ajax
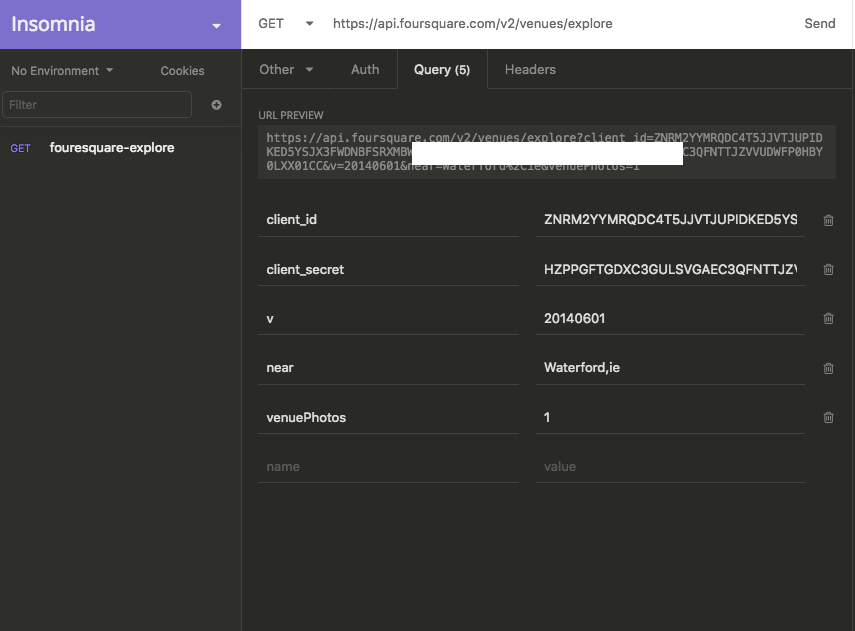
Review the FoureSquare api and the venues end point. Show how the browser, a dedicated rest tool and a node programme can access this API
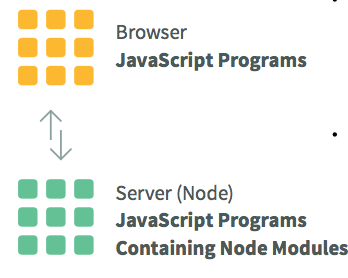
What is node? What is its role in modern development? We look at some key characteristics of the platform
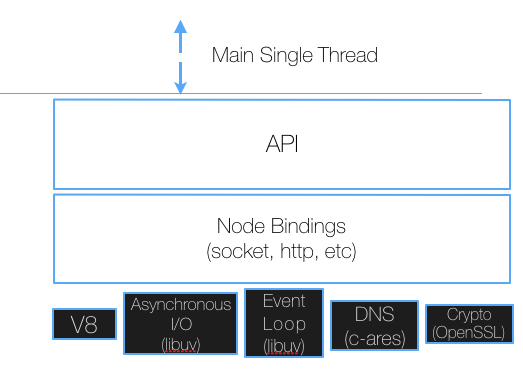
A look at the components of node, its versioning systems, and key advantages
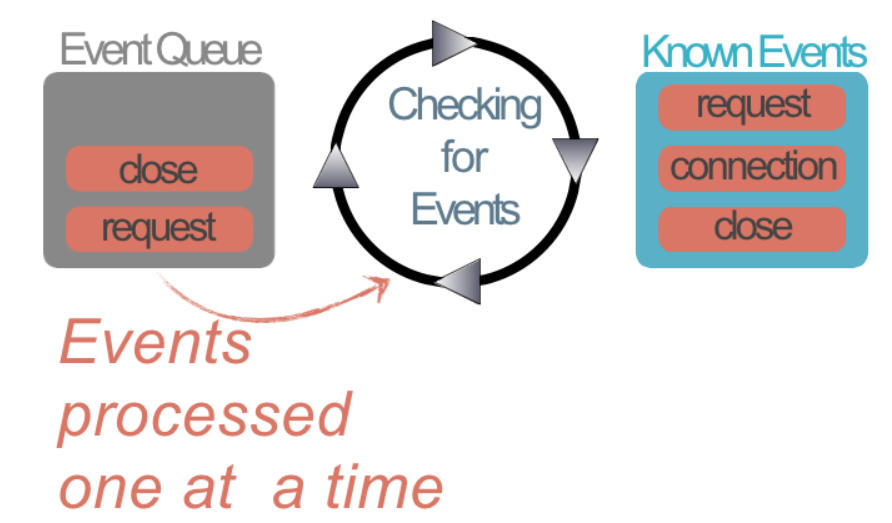
Examine how node is programmed. Explore callback styles, modules and node program structure.

The CA plans for Enterprise Web Development and Mobile Application Development
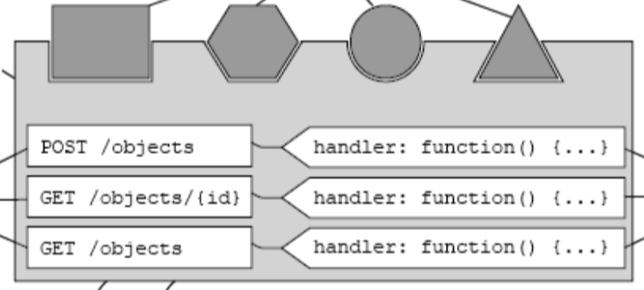
Enumerate the core building blocks of hapi and explain how these are assembled into a simple application.
Explore how to server simple views using the Hapi Inert plugin

Extend the static view with more dynamic capabilities with the vision plugin and the handlebars templating engine.

A review of the exercises in the last lab + a tour of the freecodecamp javascript lesson plan

Introduce Hapi, positioning it within the spectrum for Node Frameworks. Identify Hapis' unique features.
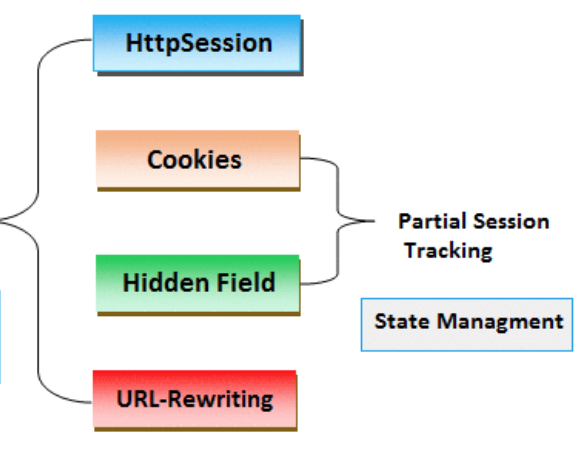
Keeping track of the currently logged in user is a challenge - as HTTP is, by definition 'stateless'. Hidden form fields, url rewriting and cookies are three common techniques for implementing sessions.
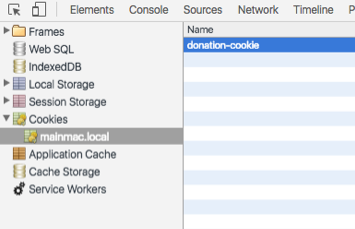
The hapi-auth-cookie provides cookie management for Hapi applications, facilitating creating, read and delete of secure browser based cookies.

Brief discussion on arrays and global variables.

A short introduction to Promises, a new feature is ES6, to simplify asynchronous programmming.

A review of the NoSQL movement and some of its key characteristics

Installing, connecting to and initialising Mongoose/MOngo db from a node application.
Creating and using Objects in Mongo, using its promise based API
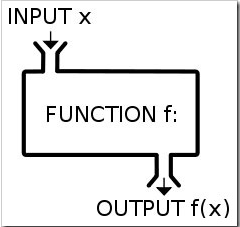
Exploring some of the expressive features of the language, such as functions as first class objects. Brief encounter with some of the newly introduced functionaliy as part of ECMAScript 2015 (ES6).
Joi is a node validation module providing general purpose schema based validation.
Hapi & Joi can work together to deliver easy to configure declarative validation for handlers.
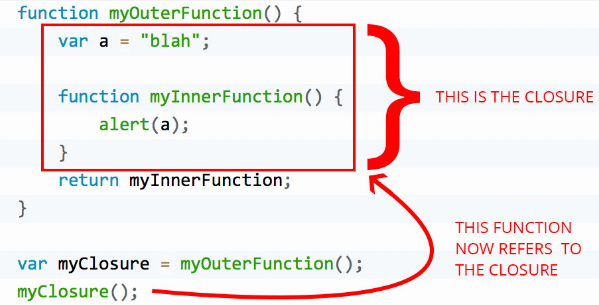
Examining closure and scope

Callbacks are gradually being replaced with Promises in some modules and components. We review callbacks again here and look at how promises approach the same tasks.

Heroku is a PaaS, supporting node and a variety of other application types. We review here the steps involved in deploying a node app.
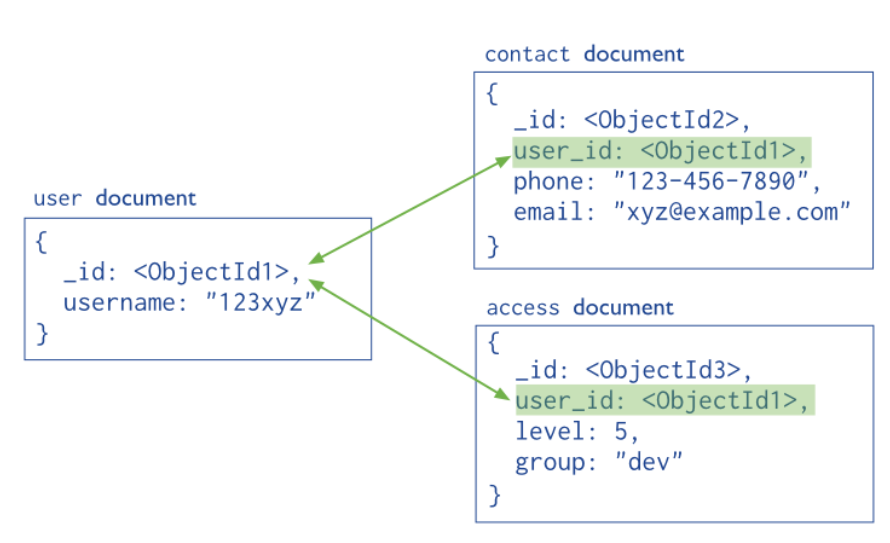
Creating and maintaining relatopnships between mongo documents enable powerful models to be constructed and queried.
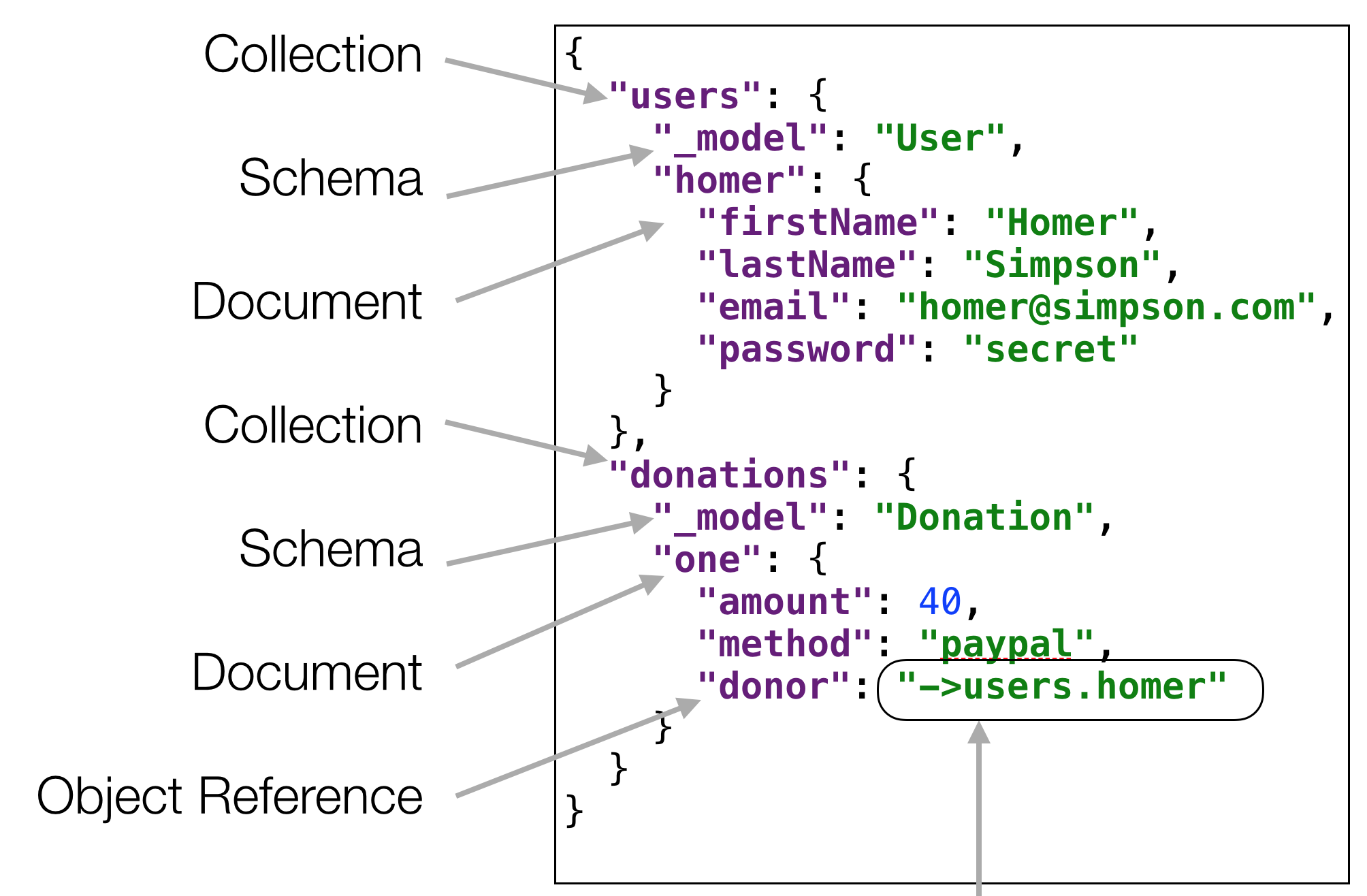
Seeding the database can simplify exploratory development, prepopulating the database with simple test data during development.
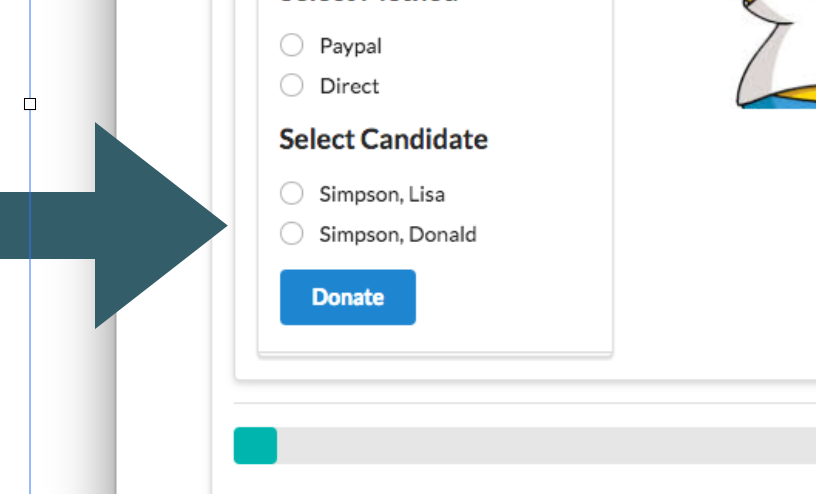
Users should be able to donate to different candidates. We extend the model to include Candidates, incorporating candidate references into donations.

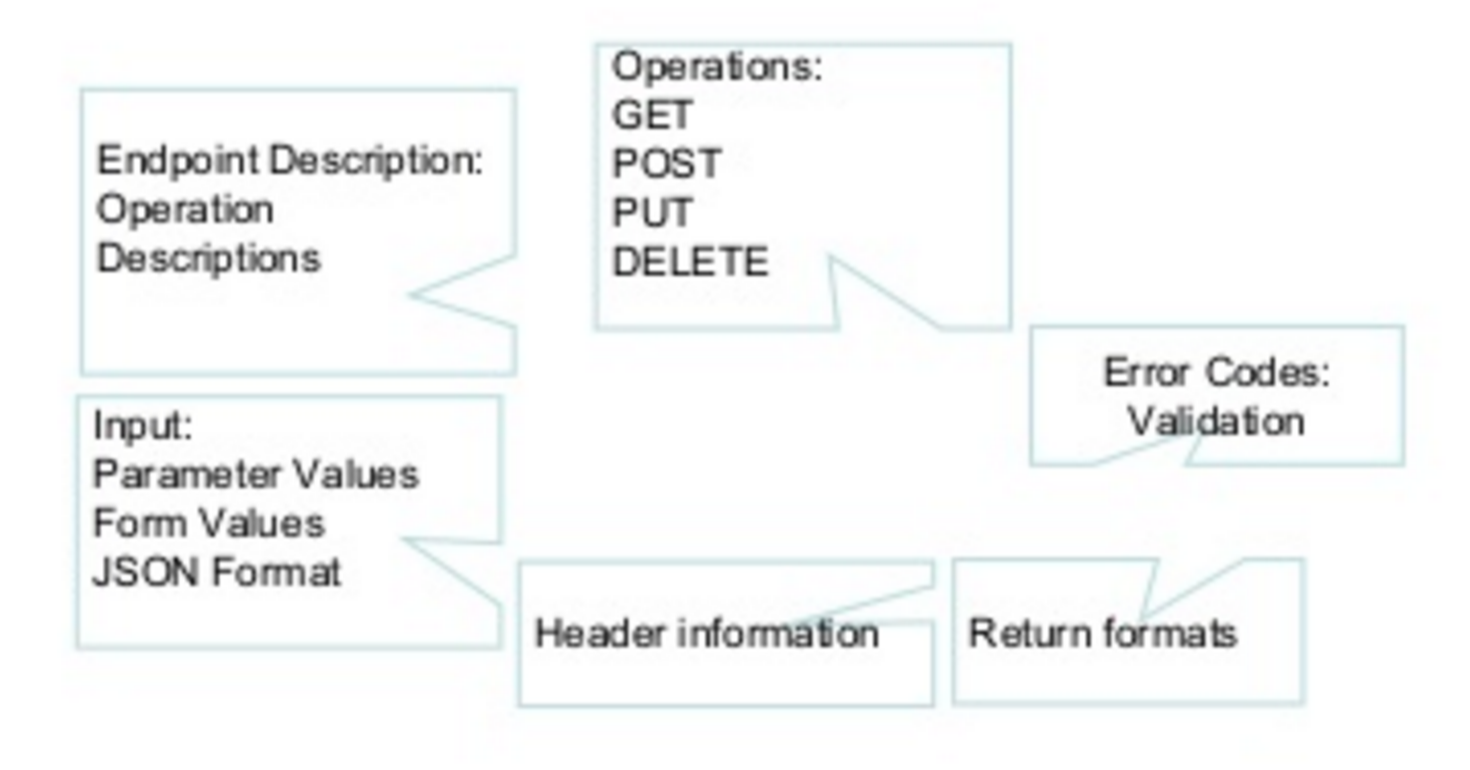
An Application Programmer Interface is the published set of http endpoints and messages that a service can support. API design and implementation is a rich field of study - here we take a general overview.
Expose access to the Candidates model as a REST endpoint. This involved defining new routes and handlers, which respond simple JSON representations.

Tools like Postman and Insomnia usefully exercise endpoints. However, we can also exercise them problematically, which offers some significant advantages.
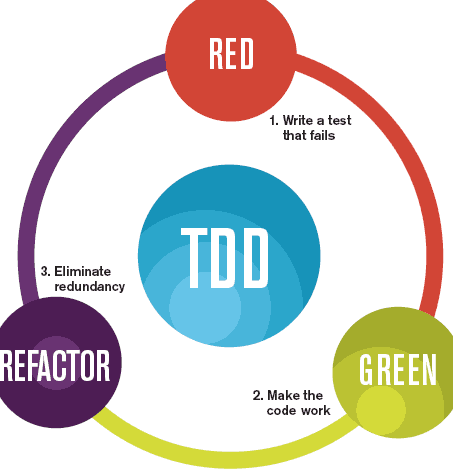
Testing is now considered an integral part of the programmers job. TDD is a technique that promotes reasonable simple unit test as precursor to implementation, significantly enhancing the robustness of the classes under test.
The essential elements of TDD are fairly easy to grasp. The support libraries (xUnit) are relatively straightforward, and we can expect our IDE to provide direct assistance to using these libraries. Here we look at the facilities Eclipse provides to the JUnit library.

One way of becoming familiar with TDD is to explore some simple examples of various strategies that might be employed in some simple examples. Here we look at useful examples from the Pragmatic series - which laid out much of the early exploration of TDD.
Accessing http and the donations api can be encapsulated in purpose built classes. We can then simplify the tests significantly, and expand them to be a more comprehensive exercise of the API.
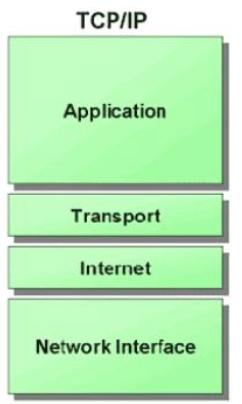
HTTP is the heartbeat of the Web, and the key protocol through with both applications and services communicate. A general understanding of it is a key part of a developers knowledge base.
Completing the Donation API involves constructing more complex so called 'Restful' endpoints, which serve to introduce references between entities in our model.

A review of the fundamental features of the Aurelia framework.
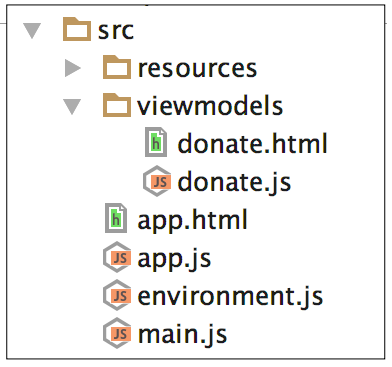
Building a first aurelial app using the aurelia-cli + webstorm. Explore the basics of viewmodels, views + binding.
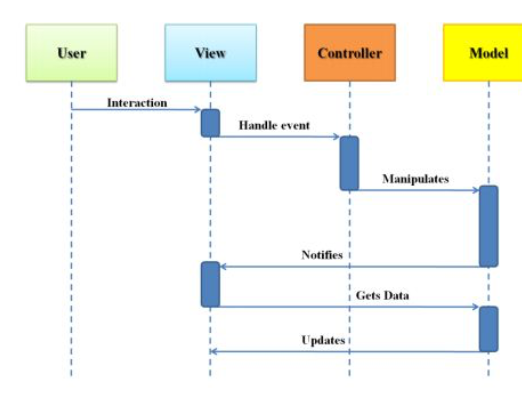
MVC & MVVM are patterns that layout potential approaches to GUI application development.
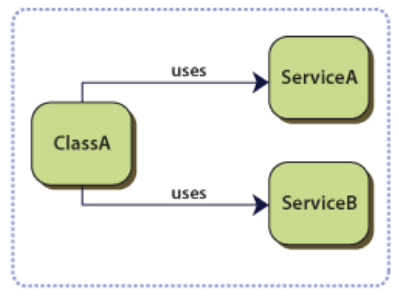
Imports & Decorators are ESNext features that are central to Aurelia. In particular they are used to pwoerfull effect to realise Dependency Injection capabilities.
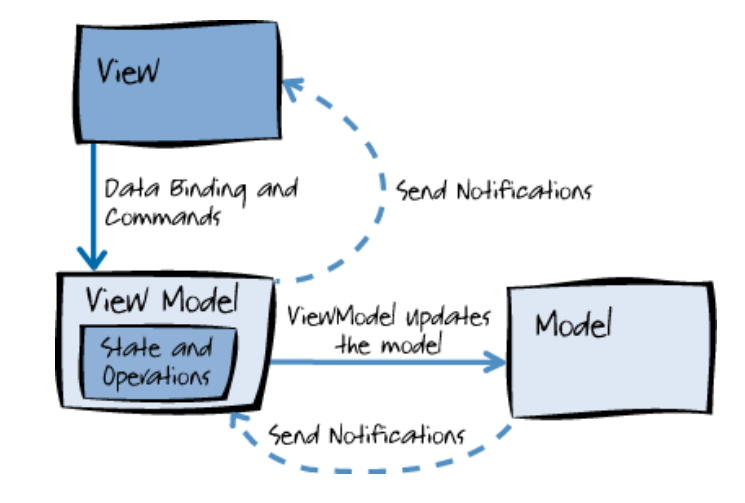
Walk through the MVVM patterns as implemented in Aurelia
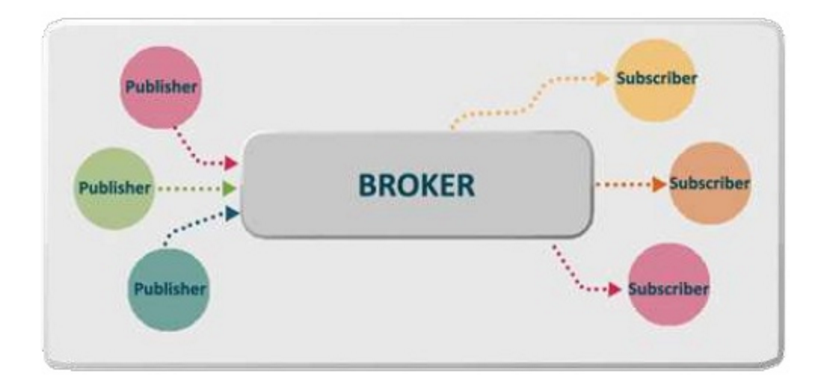
A simple Pub/Sub mechanism for Aurelia
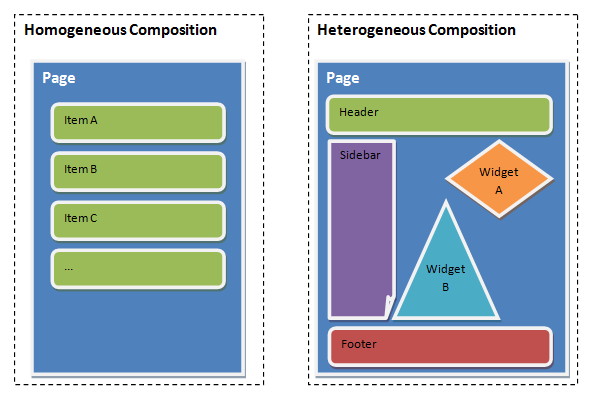
View-Models can be composed from other view-models, creating a reusable ecosystem of pluggable building blocks.,
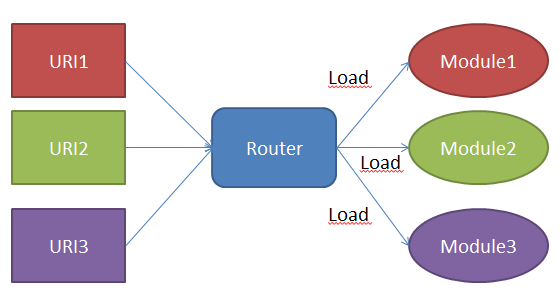
Client side routing in Aurelia
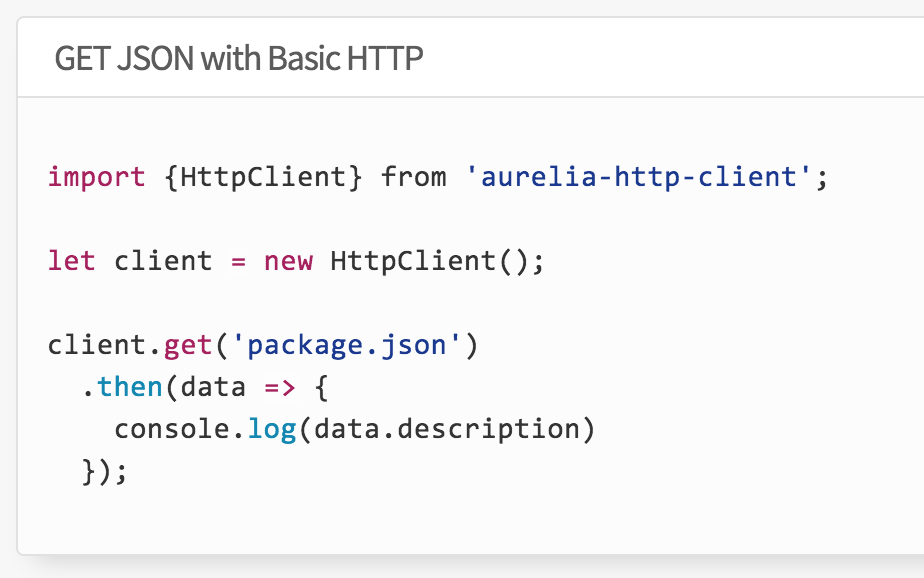
This is a component in the Aurelia framework which delivers http client access. We will need some work on the server for it to be accessed from an aurelia client.

The class can now be reimplemented to use the aureli-http-client. Existing data binding relationships should not need to be changed.

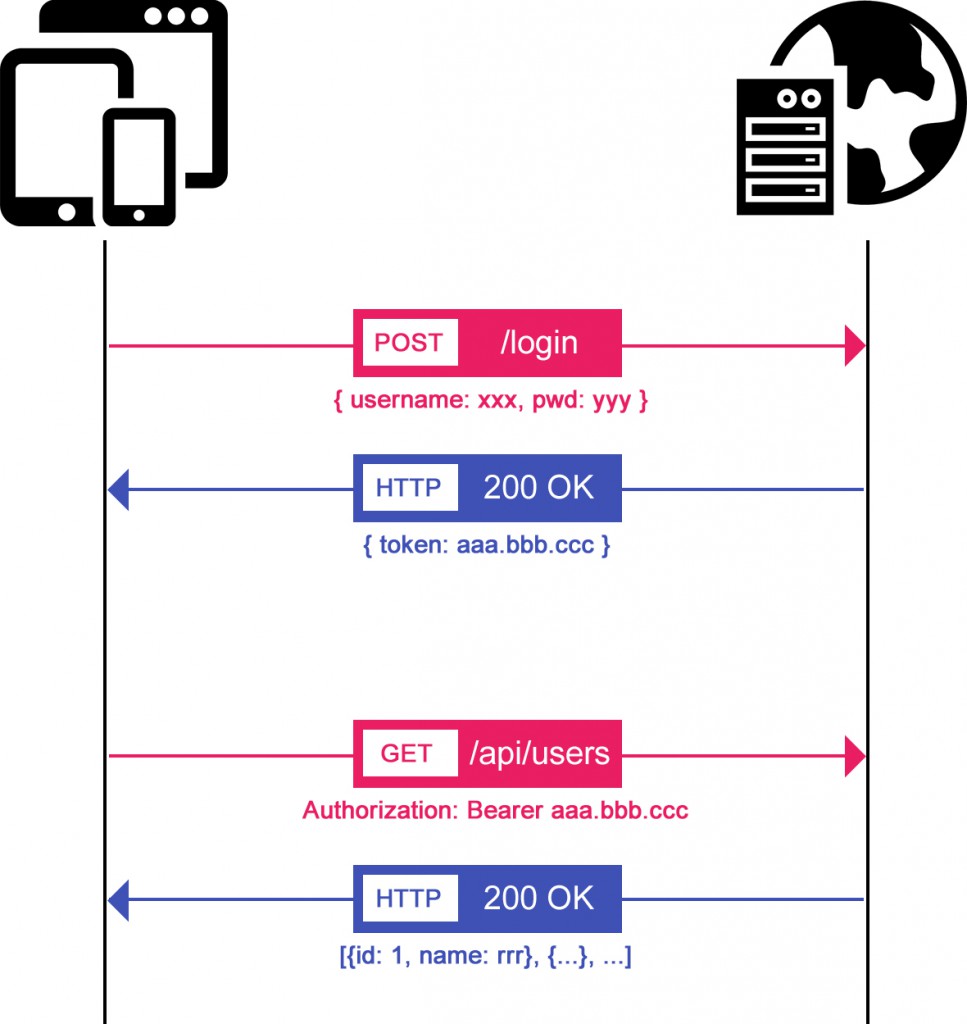
Json Web Tokens is a prominent authentication mechanism securing APIs. A review of its general principles.
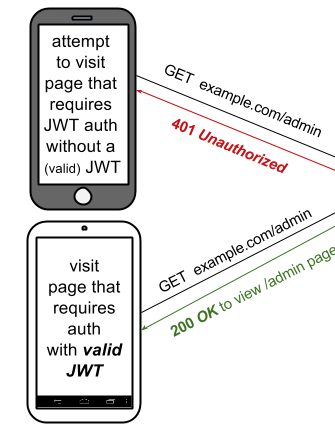
Integrating JWT into an API built using HAPI.
Incorporating JWT authentication into the Aurelia clients
A standard Java project to implement a JUnit set of tests of the donation Service API. This is essential to ensure the stability and robustness of the REST interface.
Rework the android donation application to access and update the REST interface exposed by donation-service.

Including jwt secured api access into the Android apps.
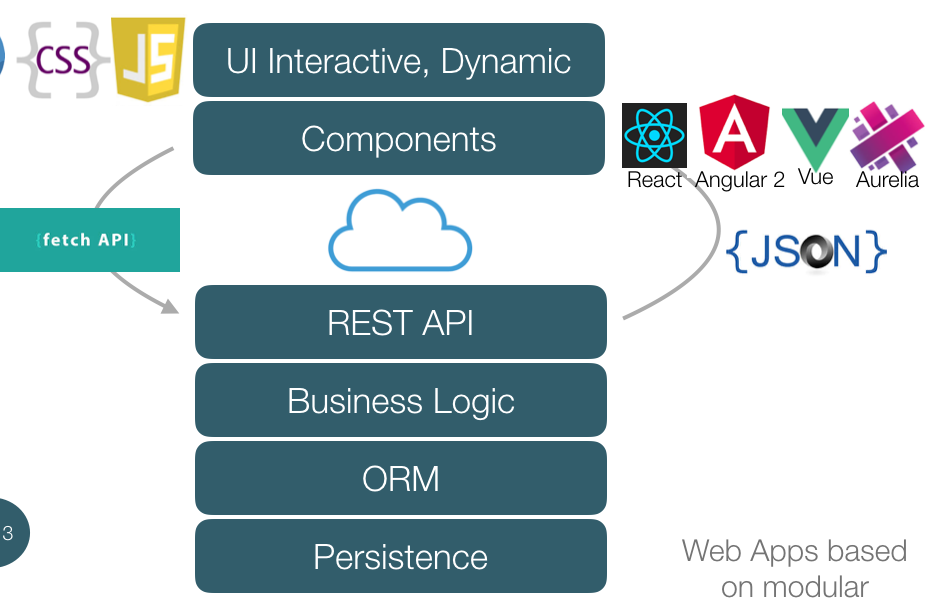
A look back at the evolution of web applications and their tools.
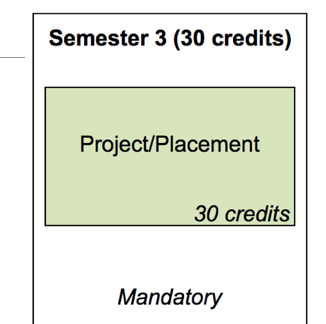
An outline of the scope and timelines of work placement project